C Signal Slot Library
- C Signal Slot Library App
- Boost Signal Slot
- C Signal Slot Library Overdrive
- C Signal Slot Library Games
- C++ Signal Slot
The C library function void (.signal (int sig, void (.func) (int))) (int) sets a function to handle signal i.e. A signal handler with signal number sig. Open mainwindow.ui in the design mode. Switch to the signals/slots mode using Menu-Edit-Edit Signals/Slots. Click and hold the widget and drag it to the window (the cursor will become an electrical ground symbol) to open the connection editor. In the connection editor, edit the main window slots on the right side.
C++C Signal Slot Library App
| Language | ||||
| Standard Library Headers | ||||
| Freestanding and hosted implementations | ||||
| Named requirements | ||||
| Language support library | ||||
| Concepts library(C++20) | ||||
| Diagnostics library | ||||
| Utilities library | ||||
| Strings library | ||||
| Containers library | ||||
| Iterators library | ||||
| Ranges library(C++20) | ||||
| Algorithms library | ||||
| Numerics library | ||||
| Localizations library | ||||
| Input/output library | ||||
| Filesystem library(C++17) | ||||
| Regular expressions library(C++11) | ||||
| Atomic operations library(C++11) | ||||
| Thread support library(C++11) | ||||
| Technical Specifications |

|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Program termination | |||||
| |||||
| Communicating with the environment | |||||
| Signals | |||||
| Signal types | |||||
| Non-local jumps | |||||
| Types | |||||
Defined in header <csignal> | |
/*signal-handler*/* signal(int sig, /*signal-handler*/* handler); | (1) |
extern'C'using/*signal-handler*/=void(int);// exposition-only | (2) |
Sets the handler for signal sig. The signal handler can be set so that default handling will occur, signal is ignored, or a user-defined function is called.
When signal handler is set to a function and a signal occurs, it is implementation defined whether std::signal(sig, SIG_DFL) will be executed immediately before the start of signal handler. Also, the implementation can prevent some implementation-defined set of signals from occurring while the signal handler runs.
For some of the signals, the implementation may call std::signal(sig, SIG_IGN) at the startup of the program. For the rest, the implementation must call std::signal(sig, SIG_DFL).
(Note: POSIX introduced sigaction to standardize these implementation-defined behaviors)
[edit]Parameters
| sig | - | the signal to set the signal handler to. It can be an implementation-defined value or one of the following values:
| |
| handler | - | the signal handler. This must be one of the following:
|

[edit]Return value
Previous signal handler on success or SIG_ERR on failure (setting a signal handler can be disabled on some implementations).
[edit]Signal handler
The following limitations are imposed on the user-defined function that is installed as a signal handler.
If the signal handler is called NOT as a result of std::abort or std::raise (asynchronous signal), the behavior is undefined if
| (until C++17) |
The behavior is undefined if any signal handler performs any of the following:
| (since C++17) |
If the user defined function returns when handling SIGFPE, SIGILL, SIGSEGV or any other implementation-defined signal specifying a computational exception, the behavior is undefined.
If the signal handler is called as a result of std::abort or std::raise (synchronous signal), the behavior is undefined if the signal handler calls std::raise.
On entry to the signal handler, the state of the floating-point environment and the values of all objects is unspecified, except for
On return from a signal handler, the value of any object modified by the signal handler that is not volatilestd::sig_atomic_t or lock-free std::atomic is indeterminate. | (until C++14) |
A call to the function If a signal handler is executed as a result of a call to std::raise (synchronously), then the execution of the handler is sequenced-after the invocation of Two accesses to the same object of type volatilestd::sig_atomic_t do not result in a data race if both occur in the same thread, even if one or more occurs in a signal handler. For each signal handler invocation, evaluations performed by the thread invoking a signal handler can be divided into two groups A and B, such that no evaluations in B happen-before evaluations in A, and the evaluations of such volatilestd::sig_atomic_t objects take values as though all evaluations in A happened-before the execution of the signal handler and the execution of the signal handler happened-before all evaluations in B. | (since C++14) |
[edit]Notes
POSIX requires that signal is thread-safe, and specifies a list of async-signal-safe library functions that may be called from any signal handler.
Signal handlers are expected to have C linkage and, in general, only use the features from the common subset of C and C++. It is implementation-defined if a function with C++ linkage can be used as a signal handler.
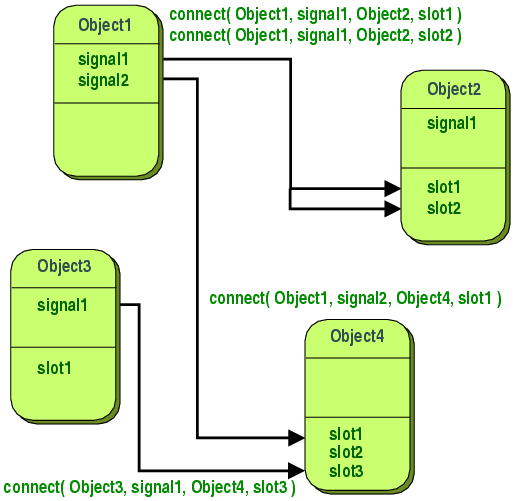
[edit]Example
Boost Signal Slot
Possible output:
[edit]See also
| runs the signal handler for particular signal (function)[edit] | |
(C++11) | fence between a thread and a signal handler executed in the same thread (function)[edit] |
- The C Standard Library
- C Standard Library Resources
- C Programming Resources
- Selected Reading
Description
The C library function void (*signal(int sig, void (*func)(int)))(int) sets a function to handle signal i.e. a signal handler with signal number sig.
Declaration
Following is the declaration for signal() function.
Parameters
sig − This is the signal number to which a handling function is set. The following are few important standard signal numbers −
C Signal Slot Library Overdrive
| Sr.No. | Macro & Signal |
|---|---|
| 1 | SIGABRT (Signal Abort) Abnormal termination, such as is initiated by the function. |
| 2 | SIGFPE (Signal Floating-Point Exception) Erroneous arithmetic operation, such as zero divide or an operation resulting in overflow (not necessarily with a floating-point operation). |
| 3 | SIGILL (Signal Illegal Instruction) Invalid function image, such as an illegal instruction. This is generally due to a corruption in the code or to an attempt to execute data. |
| 4 | SIGINT (Signal Interrupt) Interactive attention signal. Generally generated by the application user. |
| 5 | SIGSEGV (Signal Segmentation Violation) Invalid access to storage − When a program tries to read or write outside the memory it is allocated for it. |
| 6 | SIGTERM (Signal Terminate) Termination request sent to program. |
func − This is a pointer to a function. This can be a function defined by the programmer or one of the following predefined functions −
| Sr.No. | Function & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | SIG_DFL Default handling − The signal is handled by the default action for that particular signal. |
| 2 | SIG_IGN Ignore Signal − The signal is ignored. |
Return Value
This function returns the previous value of the signal handler, or SIG_ERR on error.
Example
C Signal Slot Library Games
The following example shows the usage of signal() function.
C++ Signal Slot
Let us compile and run the above program that will produce the following result and program will go in infinite loop. To come out of the program we used CTRL + C keys.